AnyDesk Remote Desktop for Linux

AnyDesk Connect to a computer remotely, The remote maintenance program from the German startup company AnyDesk Software GmbH enables remote access to remote computers. A video codec specially developed for this purpose is supposed to ensure fast transmission of the screen. It is also possible to transfer files between the two PCs. AnyDesk relies on the DeskRT video codec, which was specially designed by the developers for the transmission of graphic user interfaces. Above all, AnyDesk wants to set itself apart from competing remote desktop products such as TeamViewer and co. The program leaves a tidy impression, the address book is available with a license subject to charge.
How to install AnyDesk on Windows
The installation of AnyDesk under Windows is self-explanatory, there is a video from AnyDesk to show the setup and change settings.
How to install AnyDesk on Linux
This article describes how to install AnyDesk version 6 on Linux Mint 20 x64bit. The way to install is nearly the same for all popular Linux distributions.
Download the small AnyDesk file of 3 MB and finish urgent tasks on the go with AnyDesk’s user-friendly interface. AnyDesk are installable for Linux using the debian package manager, it’s goes quick and easy with open a terminal to insert the following lines and run it.
$ cd ~/Downloads
$ curl -O https://download.anydesk.com/linux/anydesk_6.1.1-1_amd64.deb
$ sudo dpkg -i anydesk_6.1.1-1_amd64.debIf there are errors due to dependency problems, additional packages must be installed afterwards.
package anydesk that was previously not selected is selected.
(Read Database ... 328284 Files in Folder are now installed.)
Preparing to unzip anydesk_6.1.1-1_amd64.deb ...
Failed to stop anydesk.service: Unit anydesk.service not loaded.
Unpacking from anydesk (6.1.1-1) ...
dpkg: Dependency problems prevent configuration of anydesk:
anydesk depends on libgtkglext1; or:
Packet libgtkglext1 not installed.
anydesk depends on libpango1.0-0 (>= 1.14.0); or
Packet libpango1.0-0 not installed.
dpkg: error processing package anydesk (--install):
dependency problems - leaving unconfigured
Processing triggers for gnome-menus (3.13.3-11ubuntu1.1) ...
Processing triggers for desktop-file-utils (0.23+linuxmint4) ...
Processing triggers for mime-support (3.60ubuntu1) ...
Processing triggers for hicolor-icon-theme (0.17-2) ...
Errors were encountered while processing:
anydeskThe apt-get option -fix tries to provide the packages required for AnyDesk.
$ sudo apt-get install -fThe AnyDesk installation can then take place.
$ sudo dpkg -i anydesk_6.1.1-1_amd64.debLet’s start AnyDesk also with automatic system start.
$ systemctl start anydesk.service
$ systemctl enable anydesk.serviceInstallation on Fedora and Red Hat distributions goes with yum.
$ sudo yum install anydesk_6.1.1-1_amd64.rpmThe installation using yum ends with the following output in the last lines.
Installed:
anydesk-6.1.1-1.x86_64 gtkglext-libs-1.2.0-34.fc30.x86_64 pangox-compat-0.0.2-14.fc30.x86_64
Finish.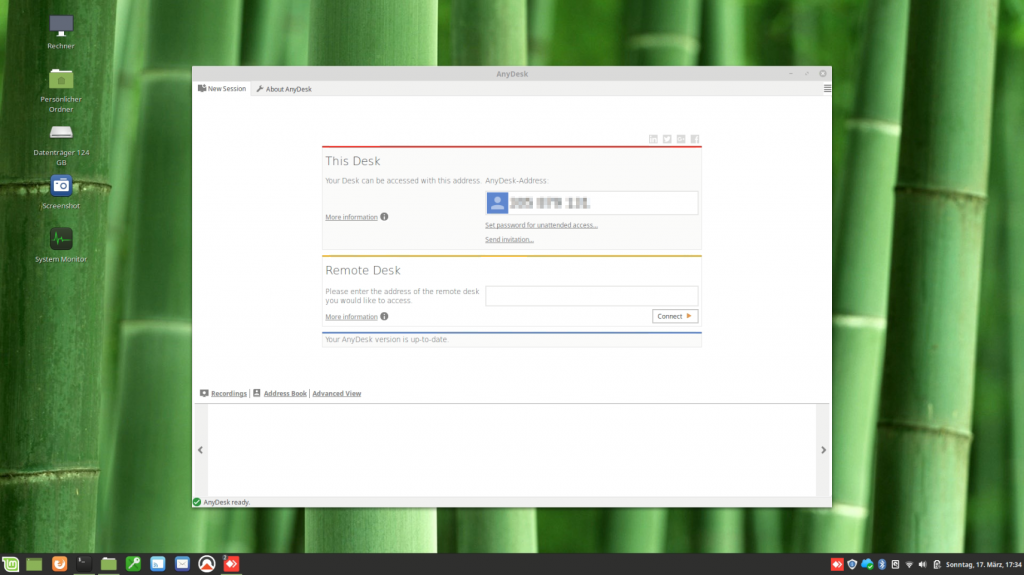
As AnyDesk announced on July 15, 2019, the binaries in the current AnyDesk version are now in the repositories for the Linux distributions Debian, CentOS, Ubuntu, RedHat Enterprise Linux, Fedora and OpenSUSE.
On Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint or other Debian-compatible Linux distributions, open a terminal and switch to root and run the following commands to install the latest version of AnyDesk:
wget -qO - https://keys.anydesk.com/repos/DEB-GPG-KEY | apt-key add -
echo "deb http://deb.anydesk.com/ all main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/anydesk-stable.list
apt update
apt install anydeskIf you use RHEL, CentOS, Fedora or OpenSUSE, open a terminal become root and copy paste one of the following section suitable for your linux distribution to add the repository. Then simply install the latest version of AnyDesk with a yum or dnf command:
# for RHEL
cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/AnyDesk-RHEL.repo << "EOF"
[anydesk]
name=AnyDesk RHEL - stable
baseurl=http://rpm.anydesk.com/rhel/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://keys.anydesk.com/repos/RPM-GPG-KEY
EOF
# for CentOS
cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/AnyDesk-CentOS.repo << "EOF"
[anydesk]
name=AnyDesk CentOS - stable
baseurl=http://rpm.anydesk.com/centos/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://keys.anydesk.com/repos/RPM-GPG-KEY
EOF
# for Fedora
cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/AnyDesk-Fedora.repo << "EOF"
[anydesk]
name=AnyDesk Fedora - stable
baseurl=http://rpm.anydesk.com/fedora/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://keys.anydesk.com/repos/RPM-GPG-KEY
EOF
# for OpenSUSE
cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/AnyDesk-OpenSUSE.repo << "EOF"
[anydesk]
name=AnyDesk OpenSUSE - stable
baseurl=http://rpm.anydesk.com/opensuse/$basearch/
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://keys.anydesk.com/repos/RPM-GPG-KEY
EOFOn CentOS run yum install anydesk, on Fedora use dnf install anydesk to install the anydesk remote desktop software.